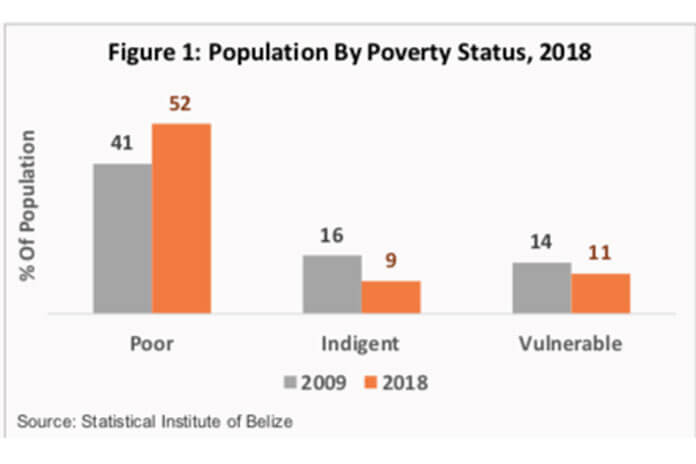
BELIZE CITY, Thurs. July 1, 2021– Yesterday, the Statistical Institute of Belize released the results of its 2018/2019 poverty study and announced that an alarming 52% of the country’s population, or 201,616 persons, were living in poverty at that time. Around 9% of the population — 35,663 persons — were considered indigent or critically poor.
The SIB report states, “About 11 percent or 42,590 persons were classified as vulnerable to poverty in 2018. These were persons who were ‘not poor’ but were at risk of falling into poverty if they experienced some type of economic shock or natural disaster.”
Such an economic shock occurred after the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic. The study, carried out before the outbreak of the global pandemic, shows that almost 42,590 persons, 11% of the population, were living at the edge of poverty before the COVID-19 outbreak. This closely parallels the roughly 42,500 applications for COVID-19 relief that the government reported that it received.
In 2009, when the last Country Poverty Assessment exercise was done, the percentage of the population living in poverty had stood at 41%, or 136,640 persons. The percentage of the population living in poverty thus increased by 11 percentage points over a 9-year span.
It is worth noting that there was an increase in the poverty rates in both rural and urban areas when compared to the numbers in 2009. In rural Belize the 2018 poverty rate, which was recorded as being 55% in previous data, increased to 59% of the population. In the urban areas an increase of around 15% in the poverty rates was seen — going from 28% in 2009 to 43% in 2018.

Corozal recorded the lowest poverty rate of all districts in 2018, and there was no significant increase in the poverty rate in that district when compared to the rate in 2009. In Toledo, on the other hand, there was a sharp increase in its poverty rate from 60% in 2009 to 82% in the recent study. That district’s indigence rate in 2018 was recorded at 30%.
The study showed that the highest rate of poverty by age group was observed among children in the 0-14 age group. Almost 60% of children in the country are considered poor, with around 12% being categorized as indigent — the highest rate of indigence among all age groups.
The SIB study showed that, of all ethnic groups, the highest rate of poverty could be found among the Mayan people, with 77% of their population in the country being classified as poor. At this time they are the only ethnic group with a poverty rate above the national average. The lowest rate of poverty was reported within the Creole ethnic group. The poverty rate within that group is 47%; however, that rate is 15 percentage points higher than what it was in 2009.
It is also worth noting that the poverty rate is much higher among households with 7 or more members — with 79% of those households being classified as poor and about 20% of them being indigent. The study also found a correlation between educational attainment and household poverty status. They found that household heads who have not completed any level of education had the highest level of poverty and the highest indigence rate, at 64% and 18% respectively.
In 2018, the study found that almost 43% of elderly persons were living in poverty, with the poverty rate of elderly ones who live with family members being 46%. Around 12% of elderly persons living alone were found to be critically poor.
Lastly, the SIB found that while the level of income inequality was not extreme in the country, it had increased since those levels of inequality were measured in 2009. The SIB used the GINI index to estimate that level of inequality.
“The 2018 Poverty Study also estimated the level of income inequality in the country using the GINI Index or Coefficient. The coefficient ranges from 0 to 1, with 0 representing no inequality and 1 representing complete inequality. As Figure 6 shows, the GINI Index in 2018 was 0.49, indicating that the level of income inequality in the country was not extreme. However, it should be noted that the level of income inequality has increased since 2009 when the GINI Index was at 0.38,” the SIB report states.